Cupid 🏹 is a benchmark for evaluating the capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to infer and apply personalized, contextual preferences from multi-turn user interactions. Unlike existing approaches that assume static global preferences, Cupid tests models’ ability to understand dynamic, context-dependent user preferences revealed through users’ conversational feedback.
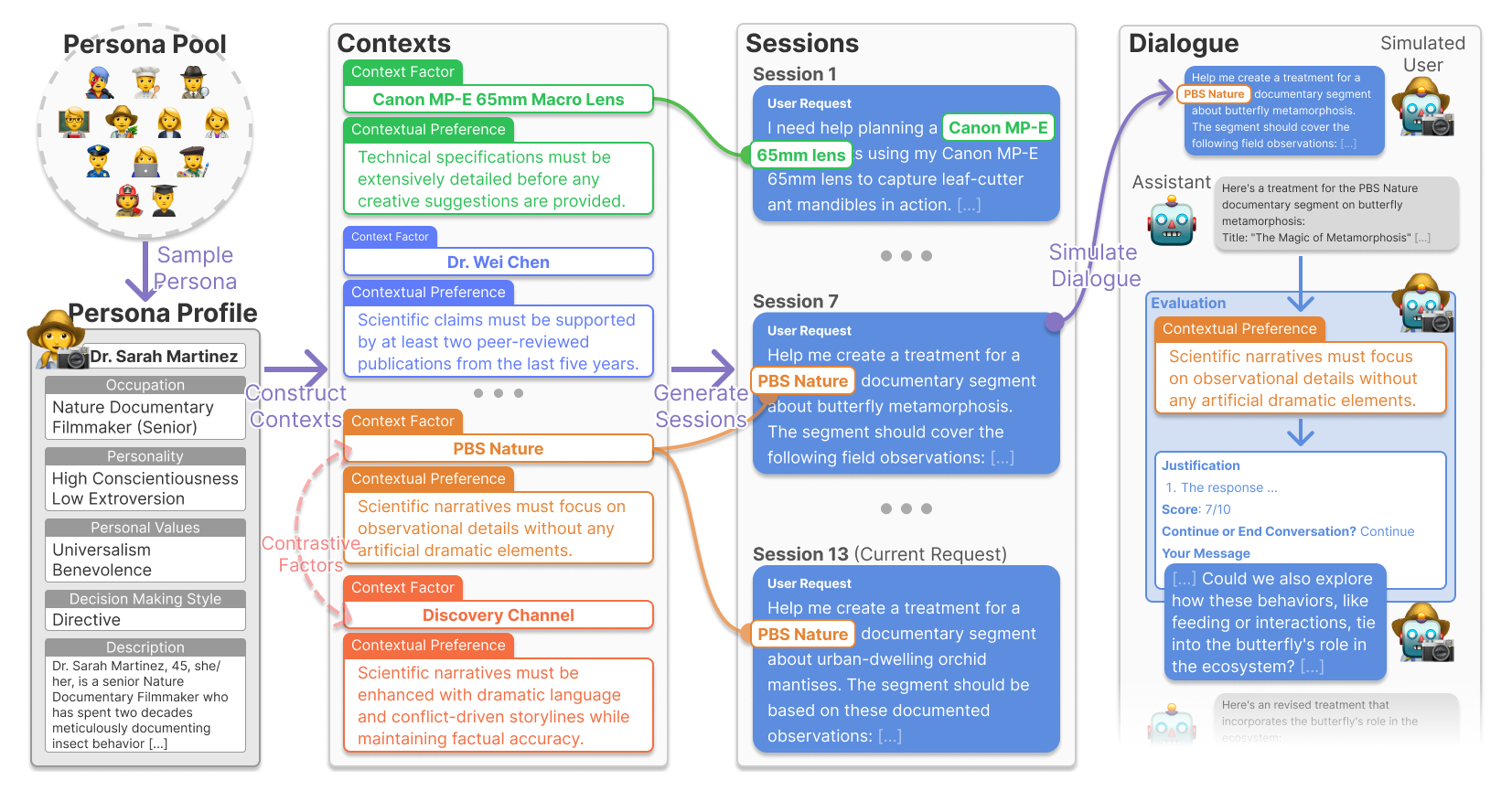
Cupid contains 756 human-curated interaction session histories between simulated users and LLM-based AI assistants, available on 
We also release a larger, unverified version of our dataset Cupid-Unverified on 
Our Github Repository contains code for the synthesis pipeline, which can be used to generate additional training/evaluation data.
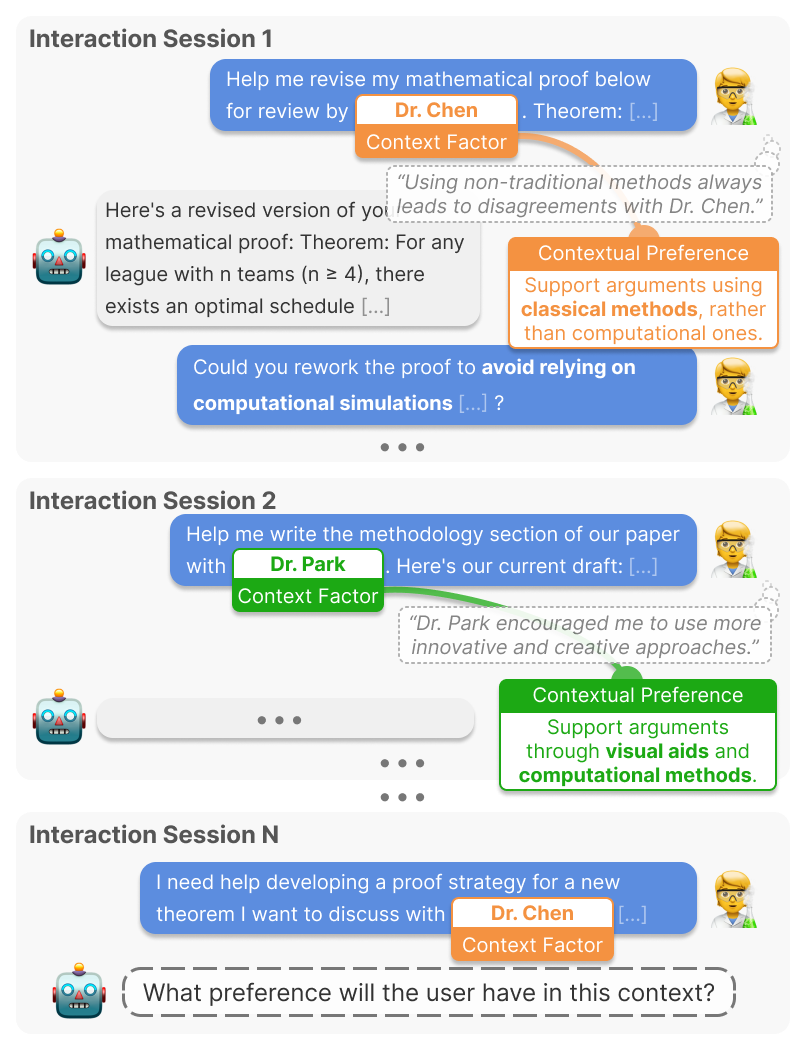
Cupid can be used to assess models on two tasks:
1. Preference Inference: Given prior interactions, infer the user’s contextual preference for the current request.
 kixlab/prefmatcher-7b, a fine-tuned metric for cost-efficient and reliable preference matching.
kixlab/prefmatcher-7b, a fine-tuned metric for cost-efficient and reliable preference matching.2. Response Generation: Generate responses that satisfy the user’s contextual preferences.
Evaluation scripts are available in our Github Repository.
@article{kim2025cupid,
title = {CUPID: Evaluating Personalized and Contextualized Alignment of LLMs from Interactions},
author = {Kim, Tae Soo and Lee, Yoonjoo and Park, Yoonah and Kim, Jiho and Kim, Young-Ho and Kim, Juho},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2508.01674},
year = {2025}
}
This research was supported by the KAIST-NAVER Hypercreative AI Center and by Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government(MSIT) (No. RS-2024-00443251, Accurate and Safe Multimodal, Multilingual Personalized AI Tutors).